In the world of fluid power systems, understanding the differences between air fittings and hydraulic fittings is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and safety. Both types of fittings play essential roles in their respective applications, but they are designed for different purposes and operate under varying conditions. Air fittings are primarily used in pneumatic systems that utilize compressed air, while hydraulic fittings are tailored for high-pressure liquid applications. This article will delve into the various aspects of air and hydraulic fittings, addressing common questions and providing insights that can help you make informed purchasing decisions.
1. Understanding Air Fittings
1.1 What are Air Fittings Used For?
Air fittings are primarily used in pneumatic systems, where they connect hoses, tubes, and other components to transport compressed air. These fittings play a vital role in powering tools, machinery, and equipment across various industries, including manufacturing, automotive, and construction. Common applications include:
- Pneumatic Tools: Air fittings are crucial for connecting tools like impact wrenches, nail guns, and spray guns, allowing them to operate efficiently.
- Control Systems: In automated systems, air fittings help control the movement of actuators and cylinders, enabling precise operations.
- Spray Equipment: Air fittings are used in paint sprayers and other spray equipment to ensure a consistent flow of air for optimal performance.
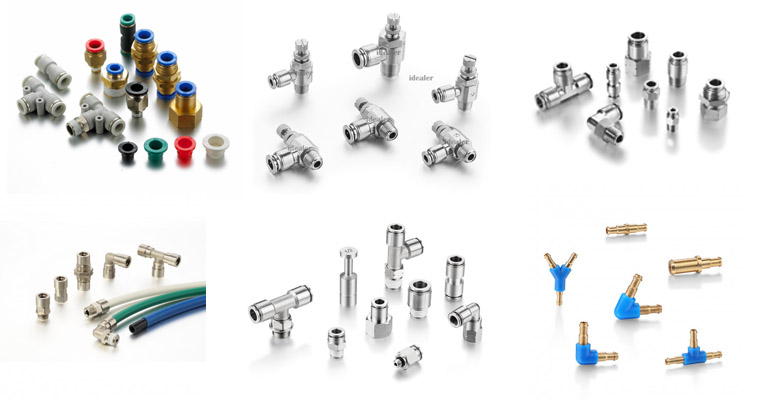

1.2 Common Types of Air Fittings
Familiarity with the various types of air fittings can help you choose the right components for your pneumatic system.
Common types of air fittings include:
| Fitting Type | Description | Advantages |
|---|---|---|
| Barbed Fittings | Used for connecting hoses, creating a secure grip. | Simple installation, good for low-pressure applications. |
| Quick-Connect Fittings | Allow for easy and fast connections without tools. | Ideal for applications requiring frequent disconnection. |
| Threaded Fittings | Require tools for installation, providing a secure connection. | Suitable for permanent installations. |
Understanding the different types of air fittings can help you select the best option for your specific application.
2. Understanding Hydraulic Fittings
2.1 What are Hydraulic Fittings Used For?
Hydraulic fittings are designed for high-pressure applications, ensuring the safe and efficient transfer of hydraulic fluids.
Hydraulic fittings are specifically engineered for use in hydraulic systems, where they connect hoses, pipes, and other components to transport hydraulic fluids under high pressure. These fittings are critical in applications such as:
- Heavy Machinery: Hydraulic fittings are essential in construction and agricultural equipment, where they facilitate the operation of hydraulic cylinders and motors.
- Automotive Systems: In vehicles, hydraulic fittings are used in braking systems, power steering, and transmission systems to ensure reliable performance.
- Industrial Equipment: Many manufacturing processes rely on hydraulic systems, making hydraulic fittings vital for machinery operation.
2.2 Common Types of Hydraulic Fittings
Knowing the various types of hydraulic fittings is essential for ensuring compatibility and performance in hydraulic systems.
Common types of hydraulic fittings include:
| Fitting Type | Description | Specific Uses |
|---|---|---|
| Flared Fittings | Create a strong seal by flaring the end of the tubing. | Suitable for high-pressure applications. |
| Compression Fittings | Use a compression ring to create a tight seal. | Often used in hydraulic lines. |
| O-ring Boss Fittings | Provide a reliable seal using an O-ring. | Commonly found in hydraulic systems. |
Selecting the appropriate type of hydraulic fitting is crucial for maintaining system integrity and performance.
3. Key Differences Between Air and Hydraulic Fittings
3.1 Pressure Ratings
Pressure ratings are a critical factor when comparing air and hydraulic fittings. Air fittings typically have lower pressure ratings, often ranging from 100 to 250 PSI, while hydraulic fittings are designed to handle much higher pressures, often exceeding 3,000 PSI.
| Fitting Type | Typical Pressure Rating |
|---|---|
| Air Fittings | 100 – 250 PSI |
| Hydraulic Fittings | 1,000 – 5,000 PSI |
This difference in pressure ratings means that using the appropriate fitting for your application is vital to ensure safety and functionality.

3.2 Materials Used
Air fittings are commonly made from materials such as aluminum, plastic, brass, and stainless steel, which are suitable for lower pressure applications. These materials are lightweight and resistant to corrosion, making them ideal for pneumatic systems.
On the other hand, hydraulic fittings are typically constructed from high-strength steel or stainless steel, designed to withstand the high pressures and harsh environments often encountered in hydraulic systems. The choice of material impacts not only the fitting’s durability but also its compatibility with the fluids being transported.
3.3 Connection Methods
Proper connection methods for air and hydraulic fittings are critical for maintaining system integrity and preventing leaks.
Air fittings can be connected using various methods, including:
- Quick-Connect Fittings: These allow for easy and fast connections without the need for tools, making them ideal for applications where frequent disconnection is required.
- Threaded Connections: These fittings require tools for installation and provide a secure connection, suitable for permanent installations.
Hydraulic fittings are typically connected using:
- Screw Connections: These require threading and are designed to create a tight seal under high pressure.
- Flange Connections: These provide a robust connection for larger pipes and hoses, ensuring stability and leak prevention.
It is crucial to follow manufacturer guidelines when connecting both air and hydraulic fittings to ensure safety and performance.


3.4 Sealing Mechanisms
Effective sealing is vital for preventing leaks and ensuring the reliability of both air and hydraulic systems.
Sealing mechanisms play a crucial role in the performance of both air and hydraulic fittings. In air fittings, O-rings and gaskets are commonly used to prevent leaks, while hydraulic fittings often require more complex sealing systems to withstand higher pressures.
A well-sealed fitting ensures that the system operates efficiently, reducing the risk of leaks that can lead to system failures and safety hazards. Regular maintenance and inspection of seals are essential to ensure long-term reliability.
4. Choosing the Right Fitting for Your Needs
4.1 Assessing Your Application
Evaluating the specific requirements of your pneumatic system is essential for selecting the right fittings.
When choosing fittings, it’s important to assess the specific requirements of your pneumatic system. Consider factors such as:
- Pressure: Ensure the fitting can handle the maximum pressure of your system.
- Flow Rate: Select fittings that can accommodate the required flow rate for optimal performance.
- Environment: Consider the operating environment, including temperature and exposure to chemicals.
4.2 Compatibility with Existing Systems
Ensuring compatibility with existing equipment and fittings is crucial for seamless operation.
Before purchasing new fittings, it’s essential to ensure they are compatible with your existing equipment. This includes checking:
- Thread Sizes: Ensure that the thread sizes match to avoid leaks.
- Material Compatibility: Verify that the materials used in the fittings are compatible with the fluids in your system.

4.3 Sourcing Quality Products
Finding reliable suppliers of pneumatic fittings is key to ensuring quality and performance.
When sourcing pneumatic fittings, it’s important to find reputable suppliers. Look for:
- Quality Assurance: Ensure that the products meet industry standards and certifications.
- Customer Reviews: Check reviews and testimonials from other customers to gauge reliability.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the differences between air and hydraulic fittings is essential for anyone involved in purchasing or maintaining pneumatic and hydraulic systems. By considering factors such as application, pressure ratings, materials, and connection methods, you can make informed decisions that enhance the efficiency and safety of your systems. If you have any questions or need personalized solutions for your pneumatic fitting needs, feel free to reach out for expert advice.