Table of Contents
ToggleIntroduction
Push-to-connect fittings have revolutionized various industries, from factory automation to medical devices, by simplifying pneumatic connections. However, after spending two decades troubleshooting systems and auditing manufacturing lines, I have witnessed the spectrum of experiences—from the beneficial to the outright disastrous. The most common question I encounter is: “Can I really trust these fittings?”
The answer is not a straightforward yes or no. While high-quality push fittings can significantly enhance speed and efficiency, poor choices or installation errors can lead to leaks, costly downtime, or even safety hazards. In this guide, I will share valuable insights gained from my experiences (including a cautionary factory tale), debunk prevalent myths, and provide actionable tips to ensure your system remains leak-free. Let’s dive in.
1. What Are Push-to-Connect Fittings—and Where Do They Fail?
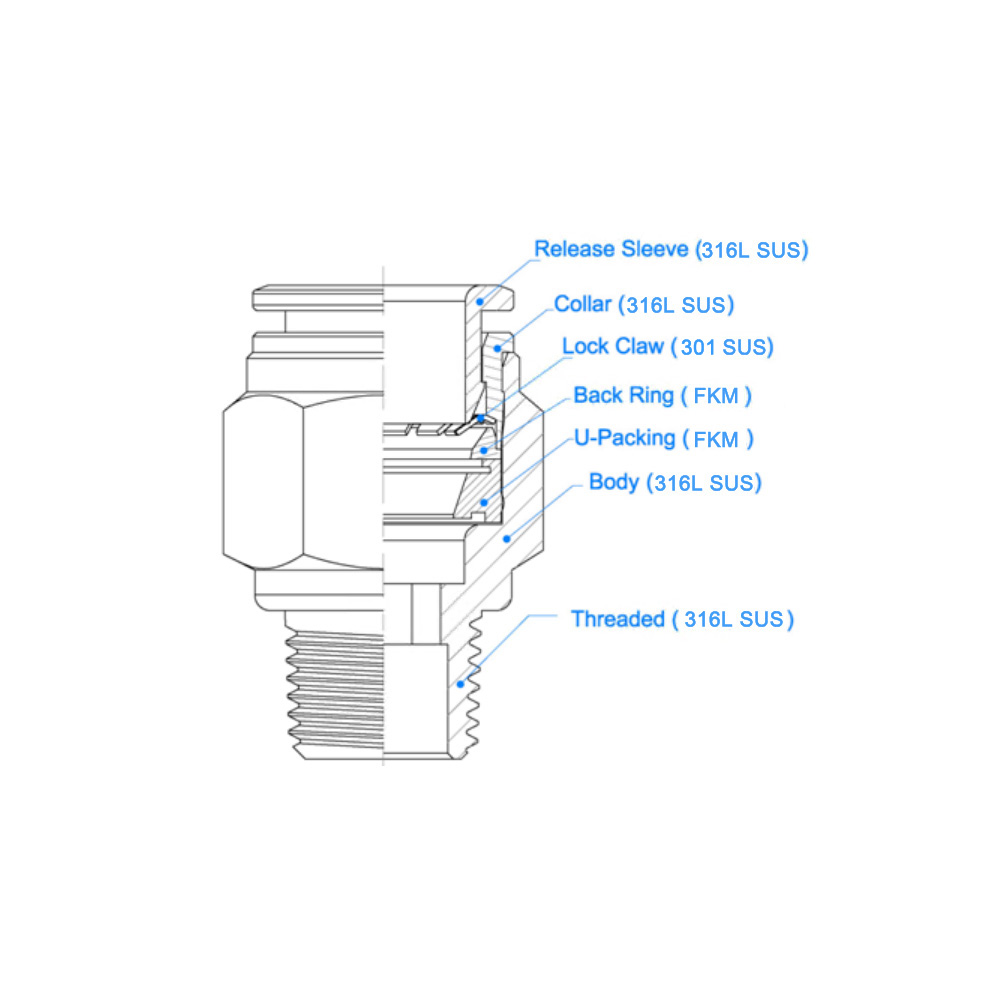
Push-to-connect fittings consist of three essential components:
- Collet: This component grips the tubing securely.
- O-ring: It provides a seal for the connection.
- Release ring: This allows for easy disconnection of the tubing.
At first glance, this seems straightforward. However, the reality is that cheap imitations often compromise quality. I have encountered collets made from brittle plastics that crack under stress and O-rings that deteriorate within months. For instance, one client opted for budget plastic fittings in a humid environment; within weeks, the O-rings swelled, leading to leaks that brought production to a standstill.
Pro Tip: Always prioritize fittings that carry ISO 9001 certification. Investing in brass or stainless steel bodies with EPDM O-rings is worthwhile for critical applications, as they offer enhanced durability and reliability.
2. “Will They Hold Under High Pressure?” The Truth About Ratings
Manufacturers often boast about pressure ratings, such as “150 PSI,” but they frequently omit a crucial detail: vibration and temperature fluctuations can reduce that rating by as much as 30%.
A packaging plant learned this lesson the hard way. They installed push fittings on a high-speed bottling line rated for 120 PSI. Within days, the vibrations from the machinery caused the collets to loosen, resulting in intermittent leaks. The solution? They switched to nylon tubing with anti-vibration sleeves and fittings featuring a reinforced collet design.
Key Takeaway:
- For high-pressure stability, use push-to-connect fittings with nylon tubing.
- Avoid using PU tubing above 100 PSI unless it is specifically reinforced for such applications.

3. Extreme Temperatures, Chemicals, and Dust: Will They Survive?
Push fittings are not universally applicable. Let’s examine the environmental risks:
Temperature:
- Standard Nitrile O-rings can crack at temperatures below -20°C or above 80°C.
- EPDM O-rings can withstand temperatures ranging from -40°C to 120°C, making them ideal for food-grade steam lines.
Chemicals:
In one instance, a chemical lab used standard fittings in an environment with solvent vapors, resulting in melted O-rings. The solution was to switch to PTFE-lined fittings, which resisted corrosion and saved the lab approximately $10,000 in downtime.
Dust/Debris:
On construction sites, dust can obstruct release rings. I recommend using threaded dust caps or flush-face couplers to protect fittings in dirty environments.
4. “Do Push Fittings Leak Over Time?” Spoiler: It’s Usually Your Fault
Yes, leaks can occur, but it’s important to note that 90% of these issues stem from installation errors, not the fittings themselves.
Common Mistakes I’ve Observed:
- Jagged tubing cuts: These can tear O-rings. Always use a tubing cutter instead of scissors.
- Over-insertion: This forces the O-ring into the collet, leading to premature wear. Mark the tubing with a pen to ensure the correct insertion depth.
- Mismatched tubing size: Using an “almost” 8mm tube in a 1/4” fitting will result in leaks.
Pro Tip: Conduct annual inspections to check for O-ring flat spots or collet wear. In high-cycle systems, consider replacing fittings every 3-5 years to maintain optimal performance.
5. When to Avoid Push-to-Connect Fittings Entirely
These fittings are not a one-size-fits-all solution. Avoid using them in the following scenarios:
- High-vibration robotic arms: In these cases, threaded or compression fittings are safer options.
- Permanent connections: Barbed fittings combined with hose clamps provide better pull-out resistance.
- Frequent disconnects: A food processing plant that replaced push fittings three times a month found that switching to quick couplers saved them $25,000 annually.


6. 5 Rules to Maximize Reliability (From My Toolbox)
- Cut tubing at a 90° angle: A $20 cutter can prevent $2,000 in leaks.
- Lubricate wisely: Apply a drop of silicone spray to the O-ring—never on the collet itself(not suitable to silicone-free application).
- Test before finalizing: Pressurize the system and perform a soap test on every joint to check for leaks.
- Match brands: Mixing brands can lead to tolerance mismatches, which may compromise performance.
- Document replacements: Keep track of fitting lifespans to anticipate potential failures.
7. The Hidden Cost of Cheap Fittings: A $50K Lesson
One client chose to use $0.50 fittings instead of $3 high quality options. Within months, leaks caused a hydraulic press to malfunction, resulting in damage to a $50,000 mold.
How to Identify Low-Quality Fittings:
- Look for rough machining marks near the O-ring groove.
- Check for loose release rings that wobble.
- Ensure there are brand markings or certifications present.
Conclusion: Trust = Right Fit + Right Habits
Push-to-connect fittings are indeed revolutionary—if you respect their limitations. Invest in quality components, adhere to best installation practices, and conduct regular inspections. When in doubt, ask yourself: “Would I bet $10,000 on this fitting?” If the answer is no, it’s time to reconsider your choice.
Need Help? Download my free Tubing & Fitting Compatibility Checklist to avoid costly mismatches.

