Table of Contents
ToggleI. Introduction
Pneumatic fittings and tubings are the backbone of many industrial and manufacturing processes, providing a reliable and efficient way to control and transfer compressed air, fluids and gases between different parts of a system. However, not all fittings and tubings are created equal, especially when it comes to high-temperature applications. In such environments, the wrong choice of fittings can lead to leaks, failures, contamination, and safety hazards, jeopardizing the efficiency, reliability, and quality of the whole process. Therefore, it is crucial to choose the right pneumatic fittings for high-temperature applications, based on a thorough understanding of the requirements, materials, design, and maintenance.
II. Understanding the Requirements of High-Temperature Applications
High-temperature applications refer to situations where the temperature of the fluid or gas being transferred or controlled exceeds the normal range of ambient temperature, typically above 100°C or 212°F. In such environments, the choice of pneumatic fittings and tubings becomes critical, as the wrong materials or design can lead to significant problems.
One of the main effects of heat on materials is expansion, which can cause fittings and tubings to loosen, leak, or even break. Conversely, when the temperature drops, materials can contract, leading to blockages or reduced flow. In addition, heat can cause materials to deform, warp, or fatigue, reducing their strength and durability. Furthermore, high temperatures can accelerate the chemical reactions between fluids and materials, leading to corrosion, fouling, or contamination.
Industries and processes that involve high-temperature applications are diverse and include aerospace, automotive, chemical, food, and pharmaceutical, among others. For example, in aerospace, high-temperature fittings are used in jet engines, where the temperature can reach over 1000°C, to control the flow of fuel and air. In automotive, high-temperature fittings are used in exhaust systems, where the temperature can exceed 800°C, to reduce emissions and improve performance. In chemical, food, and pharmaceutical industries, high-temperature fittings are used in processing and sterilization equipment, where the temperature can range from 100°C to 300°C, to ensure the safety and quality of the products.
III. Choosing the Right Materials for High-Temperature Fittings
When it comes to high-temperature applications, the choice of materials for pneumatic fittings and tubings is critical. The following are some of the common materials used for high-temperature fittings, along with their temperature limits, advantages, and disadvantages:
- Brass: temperature limit of around 200°C; good heat conductivity, corrosion resistance, and machinability; relatively low cost; may contain lead or other toxic elements; not suitable for high-pressure or high-vibration applications.
- Stainless steel: temperature limit of around 600°C; excellent heat resistance, corrosion resistance, and strength; suitable for high-pressure and high-vibration applications; relatively heavy and expensive; may require special tools and techniques for installation.
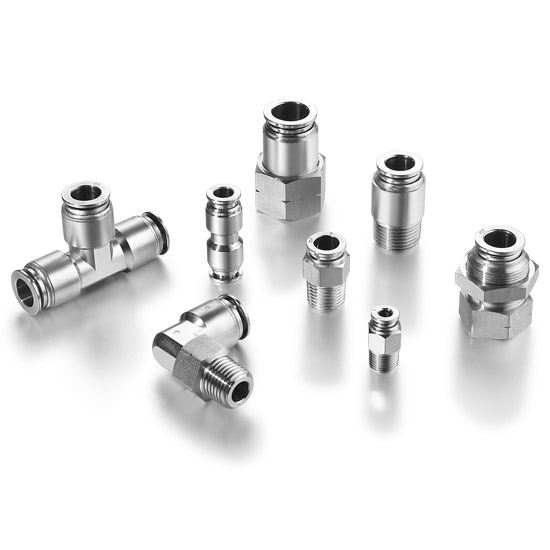

- Aluminum: temperature limit of around 250°C; good heat conductivity, lightweight, and corrosion resistance; relatively low cost; may require surface treatment or coating to improve durability; not suitable for high-pressure or abrasive applications.
- Common Plastic: temperature limit of around 150°C; lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and low-cost; suitable for low-pressure and low-vibration applications; may deform or melt under high temperature or pressure; may not be compatible with certain fluids or gases.

- PEEK (Polyetheretherketone): temperature limit of around 250°C; excellent heat resistance, chemical resistance, and mechanical properties; suitable for high-temperature and high-pressure applications; relatively expensive; may require special tools and techniques for installation.
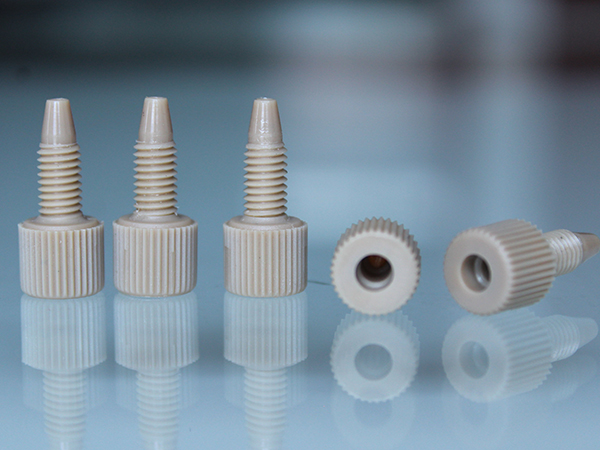

- PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene): temperature limit of around 260°C; excellent heat resistance, chemical resistance, and non-stick properties; suitable for high-temperature and corrosive applications; relatively low friction and weight; relatively expensive; may require special tools and techniques for installation.
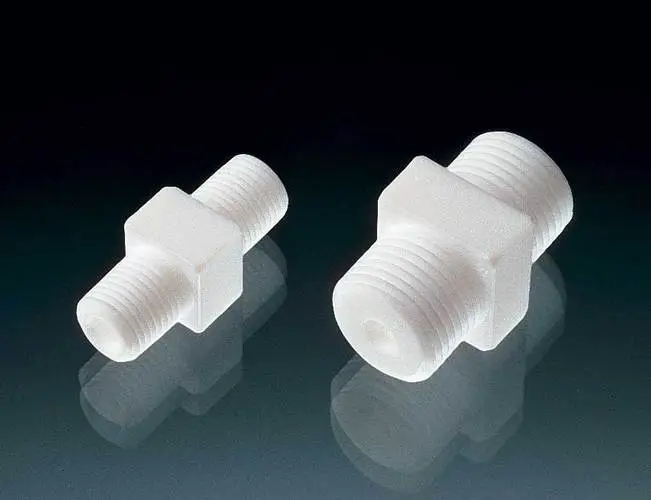

- Composite: temperature limit of around 200°C; lightweight, strong, and corrosion-resistant; suitable for high-pressure and high-vibration applications; may require special tools and techniques for installation; may be more expensive than other materials.
It is important to select materials that can withstand the highest temperature and pressure expected in the application, as well as the type of fluid or gas being transferred or controlled. In addition, factors such as corrosion resistance, weight, cost, and compatibility should also be considered. By choosing the right materials for high-temperature fittings, you can ensure the safety, efficiency, and reliability of your pneumatic system in high-temperature applications. A reputable supplier of pneumatic fittings and tubings can provide guidance and advice on the best materials for your specific needs.
IV. Considering the Design and Features of High-Temperature Fittings
In addition to the choice of materials, the design and features of pneumatic fittings and tubings also play a crucial role in their performance in high-temperature applications. The following are some of the types of fittings available for pneumatic systems, along with their characteristics and considerations:
- Push-to-connect: easy to install and disconnect; suitable for low-pressure and low-vibration applications; may not be suitable for high-temperature or high-pressure applications; may require additional sealing or locking mechanisms.

- Compression: reliable and leak-tight; suitable for high-pressure and high-vibration applications; may require more time and effort to install and maintain; may be more prone to wear and tear.

- Barb: simple and cost-effective; suitable for low-pressure and low-vibration applications; may not be suitable for high-temperature or high-pressure applications; may require additional clamps or fittings.

- Flare: reliable and leak-tight; suitable for high-pressure and high-temperature applications; may require special tools and techniques for installation; may be more expensive than other types.
- Quick disconnect: easy to connect and disconnect; suitable for frequent or temporary connections; may not be suitable for high-temperature or high-pressure applications; may require additional sealing or locking mechanisms.
When choosing pneumatic fittings for high-temperature applications, factors such as ease of installation, leak-tightness, flow rate, vibration resistance, and maintenance should be considered. It is also important to ensure that the fittings can withstand the highest temperature and pressure expected in the application, and that they are compatible with the fluids or gases being transferred or controlled.
In addition, some fittings may have additional features that can enhance their performance in high-temperature environments, such as heat shields, insulators, coatings, and seals. These features can help to reduce heat transfer, prevent corrosion, improve sealing, and prolong the lifespan of the fittings.
- Heat shields are typically made of metal or ceramic materials and are designed to protect the fittings and tubings from direct exposure to high temperatures. They can be installed around the fittings or tubings to create a barrier that reduces heat transfer and prevents deformation or melting.
- Insulators are materials that have low thermal conductivity and are used to reduce heat loss or gain. In high-temperature applications, insulators can be used to cover the fittings or tubings to prevent heat from escaping or entering the system. This can help to maintain the temperature of the fluid or gas and improve the efficiency of the process.
- Coatings are materials that are applied to the surface of the fittings or tubings to improve their resistance to corrosion, wear, or heat. Coatings can be made of various materials, such as polymers, ceramics, or metals, and can provide additional protection and durability to the fittings and tubings.
- Seals are components that are used to create a tight and leak-free connection between the fittings and tubings. In high-temperature applications, seals can be made of materials that can withstand the heat and pressure, such as silicone, fluorocarbon, or PTFE. Seals can also be designed to compensate for the thermal expansion or contraction of the fittings and tubings, ensuring a reliable and long-lasting connection.
By choosing high-temperature fittings with the right design and features, and by using additional components such as heat shields, insulators, coatings, and seals, you can improve the performance and reliability of your pneumatic system in high-temperature applications.
V. Installing and Maintaining High-Temperature Fittings Properly
Proper installation and maintenance of high-temperature fittings and tubings are crucial to ensure their performance, safety, and longevity. The following are some guidelines for installing and connecting pneumatic fittings and tubings in high-temperature applications:
- Use proper tools: use tools that are suitable for the type and size of the fittings and tubings, and that can withstand the high temperature and pressure.
- Tighten to the recommended torque: follow the manufacturer’s instructions for tightening the fittings and tubings to the recommended torque, using a torque wrench if necessary.
- Check for leaks: after installation, check for leaks by applying a leak detection solution or using a leak detector. Repeat the check periodically or after any maintenance or repair.
- Avoid kinks and bends: avoid bending or kinking the tubings, as this can reduce the flow rate, increase the pressure drop, and cause stress on the fittings.
In addition to proper installation, regular inspection, cleaning, and replacement of fittings and tubings are also important to prevent failures, contamination, and safety hazards. The following are some tips for maintaining high-temperature fittings and tubings:
- Inspect regularly: inspect the fittings and tubings for signs of wear, corrosion, deformation, or damage. Replace any components that show signs of wear or damage.
- Clean regularly: clean the fittings and tubings to remove any debris, dirt, or contaminants that can affect their performance. Use a suitable cleaning solution and follow the manufacturer’s instructions.
- Replace periodically: replace the fittings and tubings periodically, according to the manufacturer’s recommendations or based on the usage and condition of the components.
Working with a reputable supplier of pneumatic fittings and tubings who can provide technical support, customization, and quality assurance can also help to ensure the proper installation and maintenance of high-temperature fittings. A reputable supplier can provide guidance on the best materials, design, and features for your specific needs, as well as offer customization options and quality assurance.
VI. Conclusion
In conclusion, choosing the right pneumatic fittings for high-temperature applications is crucial to ensure the safety, efficiency, and reliability of industrial and manufacturing processes. The choice of materials, design, and features of high-temperature fittings and tubings should be based on a thorough understanding of the requirements, such as the temperature, pressure, fluid, and gas being transferred or controlled. Proper installation and maintenance of high-temperature fittings and tubings are also important to prevent failures, contamination, and safety hazards.
At Ideal-bell, we are committed to providing high-quality and reliable pneumatic fittings and tubings for high-temperature applications. Our team of experts can help you choose the right materials, design, and features for your specific needs, and provide technical support and customization options. Contact us today to learn more or to request a quote for high-temperature fittings and tubings.

